On October 9, 2020, Transportation Research Part C, an international authoritative journal in the field of transportation, published the research about traffic signal control based on sampled trajectory data by Professor Wanjing Ma research group. This study is applicable to low-resolution trajectory data with low penetration rate and long sampling interval, which can improve the efficiency of transportation systems in urban areas.
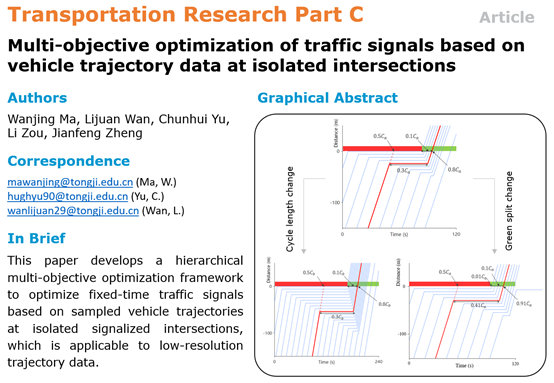
Existing fixed-time traffic signal optimization methods mainly use traffic volumes collected by infrastructure-based detectors (e.g., loop detectors). These infrastructure-based detectors generally have high maintenance costs and low coverage. With the deployment of probe vehicles, vehicle trajectory data provide more information about traffic states and can be utilized for signal timing. However, most related studies assume high penetration rates of probe vehicles or short sampling intervals, which are unlikely to be satisfied in the near future. To address the gaps, this paper develops a hierarchical multi-objective optimization framework to optimize fixed-time traffic signals based on sampled vehicle trajectories at isolated signalized intersections under both under- and slightly over-saturated traffic conditions. The aggregation of sampled trajectory data during the same period across multiple cycles and Same-ratio Principles (SRPs) are proposed to compensate for the limitations of low penetration rates of probe vehicles. The evolution of sampled trajectories with varying signal timings are formulated explicitly. Simulation studies validate the advantages of the proposed model over the one in Synchro Studio. Sensitivity analysis shows that: 1) the proposed model is applicable to Poisson vehicle arrivals; 2) the proposed model can handle sampling intervals as long as 15 s when sufficient sampled vehicle trajectories are collected; 3) the number of sampled trajectories has impacts on the performance of the proposed model instead of probe vehicle penetration rates, especially with under-saturated traffic; 4) cycle lengths of initial signal timing plans have no noticeable impacts on the required number of sampled trajectories when a short sampling interval is applied; and 5) the proposed model is insensitive to the quality of initial signal timing plans with under- and slightly over-saturated traffic. The proposed model is also implemented with field data to demonstrate its applicability in the real world.
The paper link: https://authors.elsevier.com/sd/article/S0968-090X(20)30726-9